Peridontal disease explained
What is periodontal disease?
Periodontal disease, also referred to as periodontitis, is an oral health condition that can have serious consequences if left untreated. Periodontitis, the advanced stage of gum disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects the supporting structures of your teeth, such as the gums, bones and connective tissues. It’s crucial to understand the signs, causes and treatment options for periodontal disease to protect your overall oral health.
Stages of gum disease
Gum disease progresses through several stages, each escalating in severity:
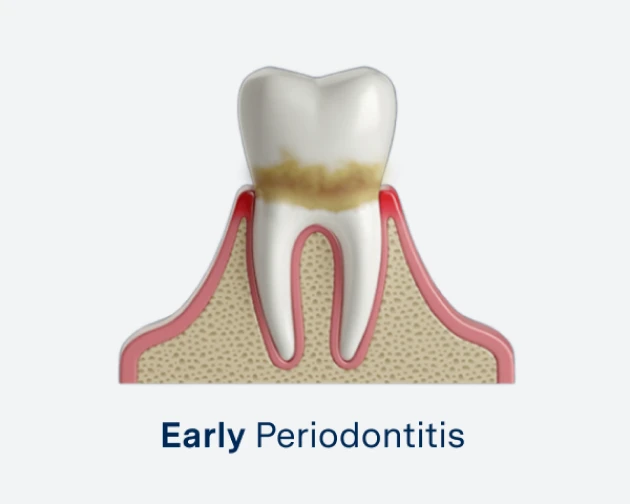
Early Periodontitis
Minor bone loss begins, and gums may start receding, forming small pockets around teeth.
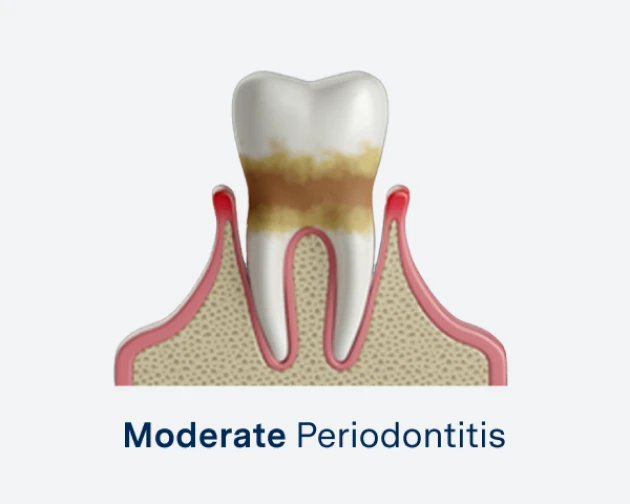
Moderate Periodontitis
Increased gum recession and deeper pockets lead to significant damage to bone and tissue.
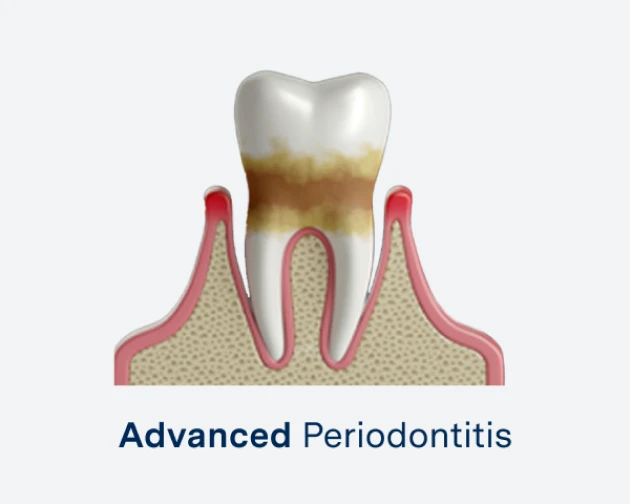
Advanced Periodontitis
The most severe stage, where teeth become loose or may be lost due to extensive damage to the supporting structures.
Causes and risk factors of periodontitis
Periodontal disease doesn’t appear out of the blue; it’s often a result of plaque buildup and influenced by several risk factors:
Plaque and tartar buildup
Tobacco use
Genetics
Health conditions
Medications
Poor diet
Autoimmune diseases
Symptoms of periodontal disease
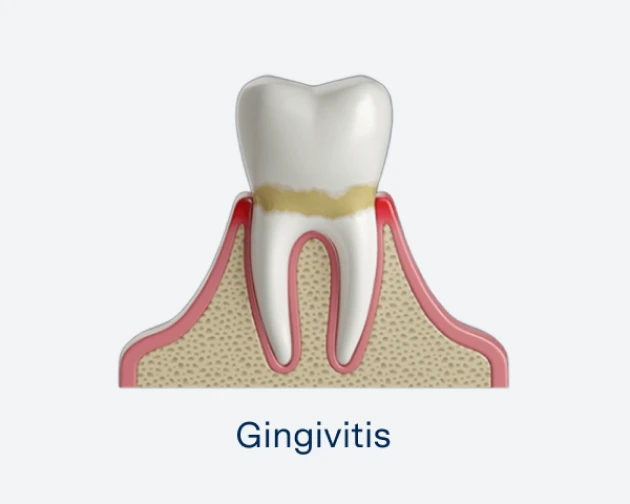
Periodontal disease often begins as gingivitis, which is characterized by red, swollen and gums that bleed easily. At this early stage, it is reversible with proper oral hygiene and routine cleanings. When gingivitis is left untreated, however, it can progress to periodontitis—a more severe form of gum disease.
As periodontal disease progresses you may experience the following symptoms:
Red, swollen or tender gums
Bleeding gums while brushing, flossing or eating
Persistent bad breath
Deep pockets forming between the teeth and gums
Loose or shifting teeth
Receding gums or teeth appearing longer than before
Changes in your bite
How to treat periodontal disease
When it comes to gum disease, there are different ways to tackle it, from periodontal cleanings (also referred to as dental deep cleanings) to more invasive treatments, based on how advanced it is.
Nonsurgical treatments
For mild to moderate cases, scaling and root planning is often recommended. This periodontal cleaning process removes plaque and tartar from beneath the gum line and smooths the tooth roots to help gums heal and reattach.
Surgical treatments
Flap surgery/pocket reduction: Helps clean out deep tartar and shape the bones and gums.
Bone grafting: Fills in where bone was lost, encouraging new growth and stabilizing teeth.
Soft tissue grafts: Fixes and builds up the gums, protecting teeth from further damage.
Guided tissue regeneration: Uses special materials to help new bone and tissue grow, and are commonly used with dental implants.
Tissue stimulating proteins: This treatment involves applying a special gel to the diseased tooth root. The gel contains proteins that stimulate healthy bone and tissue growth.
After treatment care
Post-periodontal treatment, stepping into a regimen of aftercare is crucial for keeping your gums healthy and preventing disease recurrence. Here’s a brief guide:
Periodontal disease is manageable, not curable. The bacteria that cause the disease regroup every three months, making a 3-month maintenance check-up essential to interrupt this cycle and prevent further damage.
Regular 3-month visits are vital for anyone who's undergone periodontal treatment, to avoid complications like calculus buildup and bone loss.
Your overall daily maintenance plays an important role in managing a successful post-periodontal treatment care.
Post-treatment improvements and homecare
After treatments like scaling and root planing, you may notice:
Reduced redness and discomfort
Less bleeding and tooth sensitivity
An overall healthier appearance of the gums
Improved freshness in your breath
Minimizing symptoms post periodontitis treatment
To ease into recovery and enhance treatment benefits, consider:

Diet & eating
Stick to soft, non-irritating foods initially to avoid discomfort.

Managing discomfort & sensitivity
Over-the-counter pain relief can help manage any discomfort. For sensitivity, avoid extremely hot or cold foods and drinks.

Oral hygiene
Gentle brushing and flossing are key. Your dental team may also recommend specific mouth rinses such as antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria in hard-to-reach areas.
Periodontal disease FAQs
Can periodontal disease be cured?
For mild to moderate cases, scaling and root planning is often recommended. The periodontal cleanings process removes plaque and tartar from beneath the gum line and smooths the tooth roots to help gums heal and reattach.
Can you save teeth with periodontal disease?
Absolutely. Saving your teeth is our priority. Catching the disease early and following through with treatment and home care can make a big difference. We're here to guide you on how to keep your teeth healthy and secure. Overall, with proper care and oral hygiene it is possible to keep your teeth given the right treatment plan for you.
Will I lose my teeth if I have periodontal disease?
While losing teeth may be a possibility if periodontal disease is left untreated, with timely treatment and good oral care, both at home and with regular visits to Aspen Dental, we can work towards keeping your natural teeth intact.
Can you reverse periodontal pockets?
Yes, through specific surgical treatments, we can effectively reduce the depth of periodontal pockets. Procedures like flap surgery clean out deep tartar and help gums heal closer to the tooth. Additionally, guided tissue regeneration can prompt your body to rebuild bone and gum tissue around the teeth. At Aspen Dental, we're here to explore these surgical options with you, aiming to restore your gums to better health.
How do you prevent periodontitis?
What toothpaste is best for periodontal disease?
Look for toothpaste that's formulated for gum health, with fluoride and antimicrobial ingredients.
What are the stages of gum disease?
Gingivitis: The earliest stage, marked by gum inflammation and bleeding.
Early Periodontitis: Minor bone loss and the beginning of periodontal pockets.
Moderate Periodontitis: Increased pocket depth and more significant bone loss.
Advanced Periodontitis: Severe bone loss, leading to loose teeth or tooth loss.
Managing gum health is a continuous journey, and at Aspen Dental, we're here to support you every step of the way—from prevention to treatment and beyond.
Is periodontal disease contagious?
Periodontal disease itself is not contagious, but the bacteria that cause the infection can be transmitted through saliva. Sharing utensils or kissing can expose someone to these bacteria, emphasizing the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene.
What is periodontics?
Periodontics is a branch of dentistry focused on the structures surrounding and supporting your teeth, including gums and bone. Periodontists specialize in preventing, diagnosing, and treating gum disease and placing dental implants.
Discover more for your smile
Protect your gums for a healthy smile
Routine dental visits and diligent gum care are essential to keep periodontal disease at bay. Let Aspen Dental help you maintain optimal oral health.

